Name of Medical Device
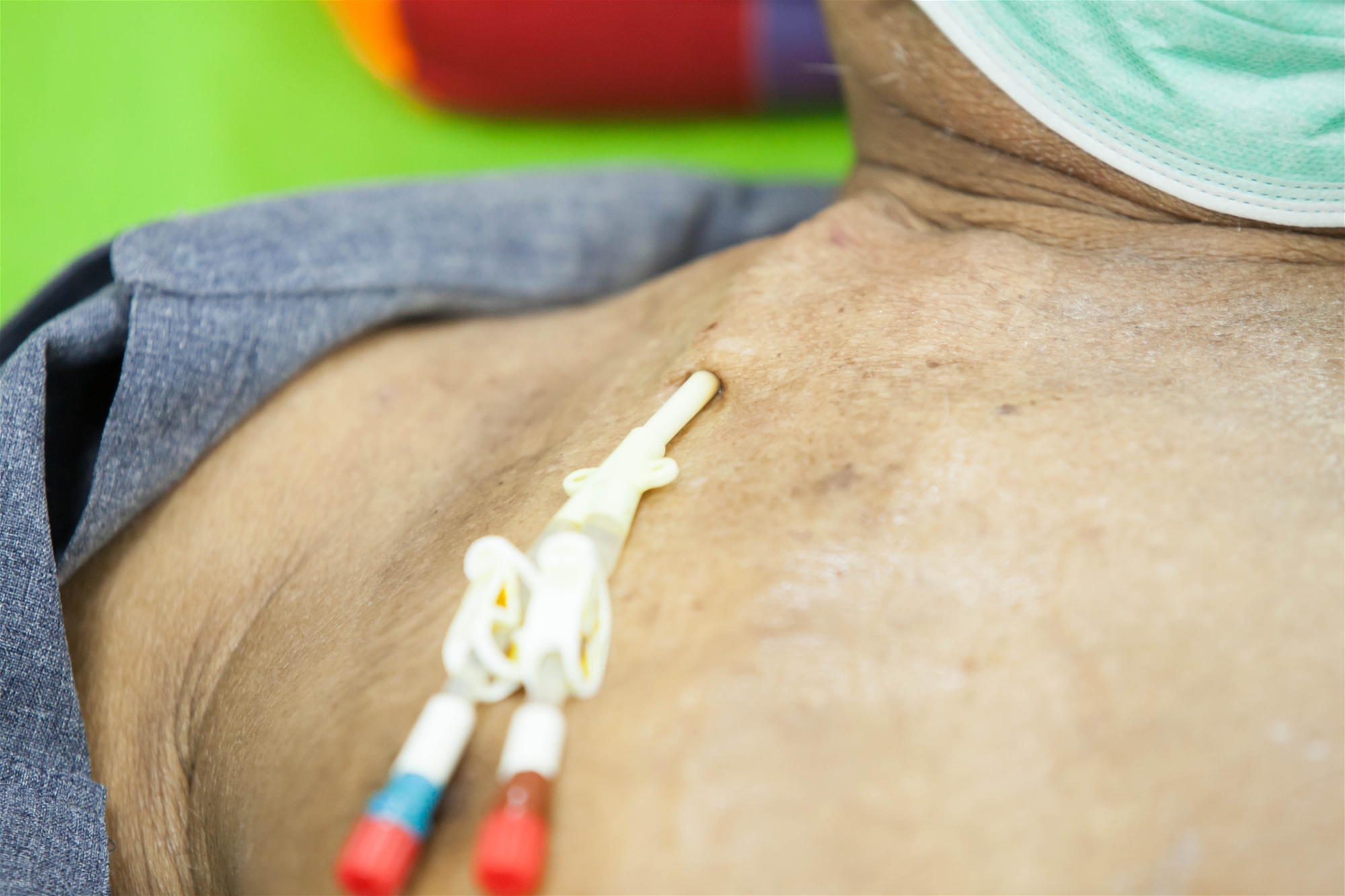
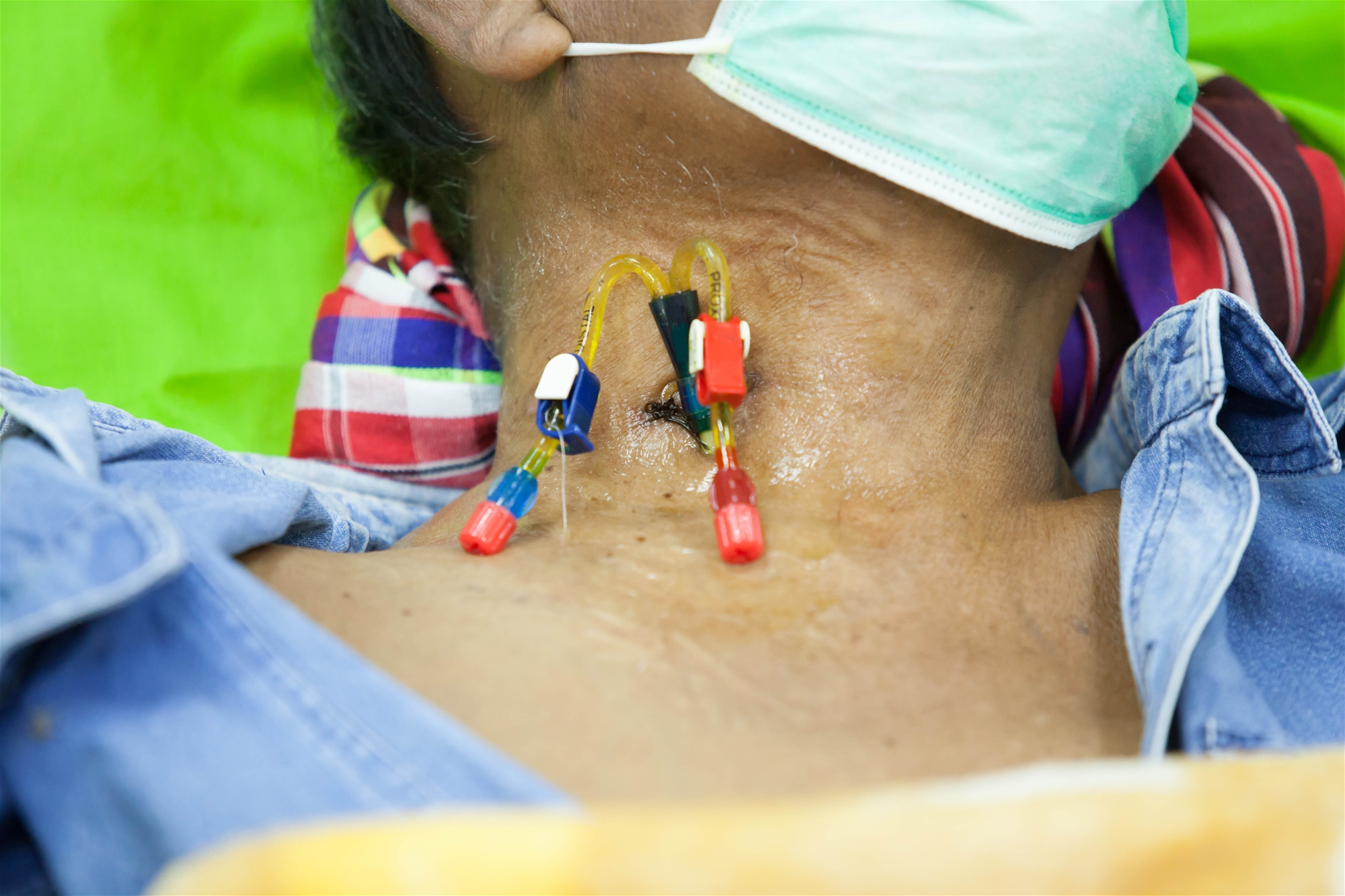
Hickman catheter or central venous catheter.
Description
Through the internal jugular vein puncture method, it provides various uses such as large diameter intravenous infusion, blood drawing and hemodialysis.
When to Use
- For those who need long-term intravenous infusion.
- Acute/chronic renal failure requires long-term hemodialysis.
Possible Side Effects
- The incidence of blood vessel rupture and bleeding during operation is < 1%.
- The incidence of pneumothorax or hemothorax during or after operation is <1%-3.5%. About a third of cases have to be treated with chest tube insertion.
- The incidence of arrhythmia during or after surgery is < 1 %.
- The incidence of wound healing failure or wound infection after operation is 1 %-2 %.
- The incidence of wound hematoma after operation is < 1%.
- The incidence of catheter infection during or after operation is 1%-3%, that of rupture is <1%, and that of displacement or obstruction is 1.5%-6%. Some patients need to undergo a reoperation to remove the catheter.
- Postoperative obstruction of the superior vena cava or femoral vein is <1 %-1.6 %. Approximately 1.5% to 3.5% of patients have to undergo surgery again to remove the artificial vessels during the course of treatment.
- Due to poor immunity, the incidence of postoperative infection is 6% in patients with hematological and neoplastic disorders and 8% for artificial blood vessel obstruction, which are all higher than that of other patients.
- During or after operation, some non-surgical, unexpected major complications (e.g. myocardial infarction, stroke or respiratory failure, gastrointestinal bleeding), sudden death or death after operation may occur because of the patient's own known or unknown diseases (e.g. cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular diseases, lung diseases, gastrointestinal disorders).
- Other incidental findings.
 |
 |
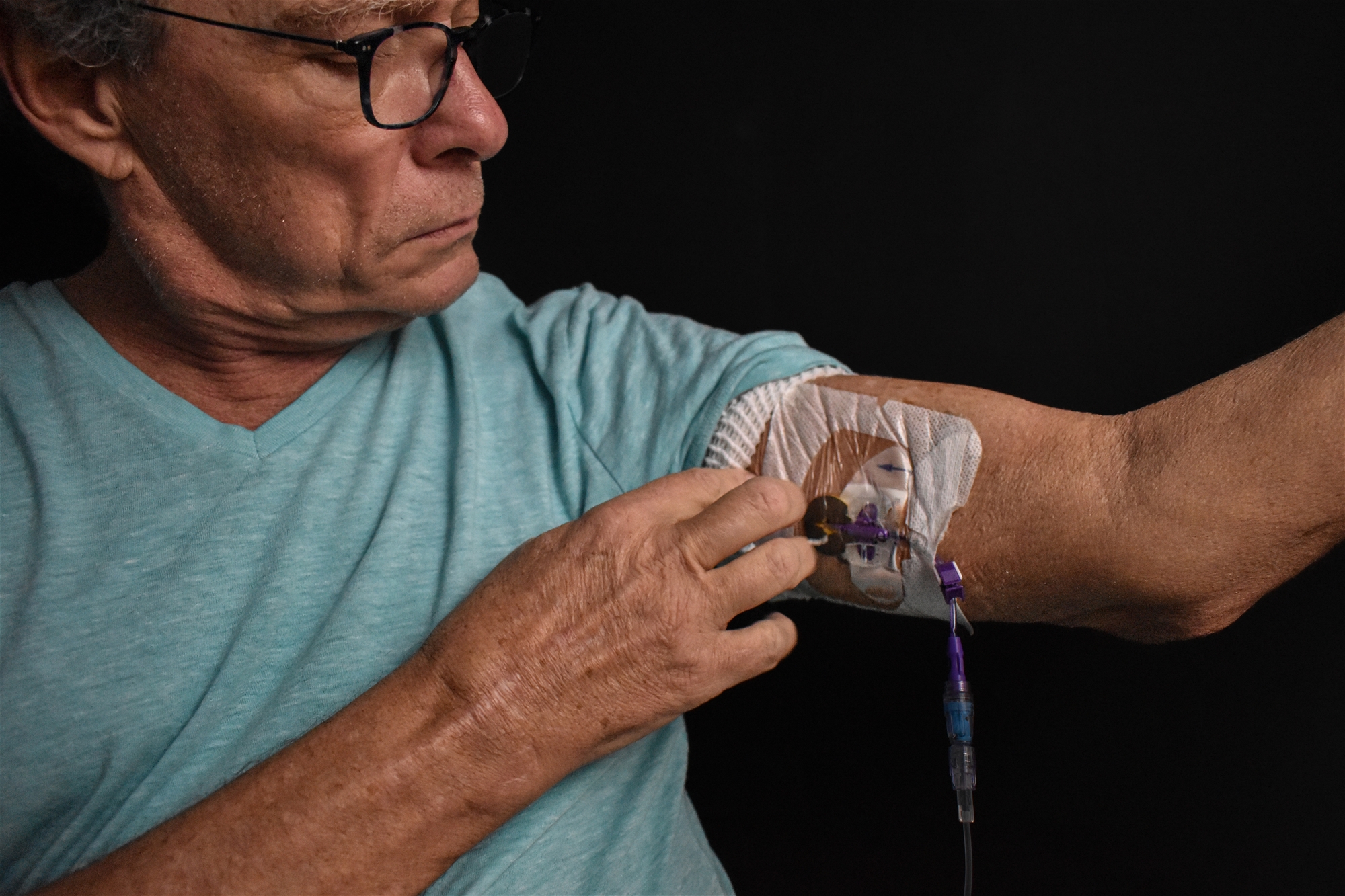 |
| Hickman catheter | CVC | PICC |
Postoperative Care
- Postoperative chest X-ray is required to confirm the location of the catheter.
- When infectious symptoms such as redness and swelling of the surrounding wound or effusion occur, return to the doctor as soon as possible for examination.
- Make regular return visits for catheter patency.
- Please make sure that your primary care provider understands the procedures of wound care and cleaning before being discharged from hospital. If you have any questions, please consult your physician or nurse practitioner for relevant information.

