Procedures
- Wash Hands Correctly.
- Assisting patient to sit up and take a semi-follow position or elevate his/her head up to 30-60 degree.
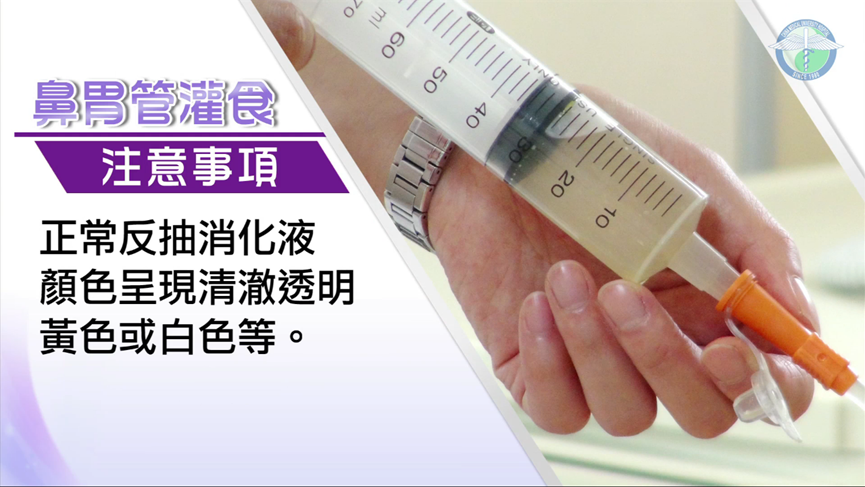
- Prior to tube feeding, double check on your patients to see if their N-G tube is in place of the stomach. Tube feeding method: insert a feeding syringe at the end of N-G tube then withdraw the syringe. If gastric acid is drawn out, it means the tube is in the stomach.
- Assessing the amount of gastric acid in stomach.
Method:insert a feeding syringe at the end of N-G tube then withdraw the syringe. If the total amount of remains in the stomach falls below 60ml, tube feeding is allowed to proceed. However, if the remains of the last feeding in the stomach seem to be over 50%, the procedure should then be postponed. Assessing the amount of gastric acid in stomach is necessary an hour later.
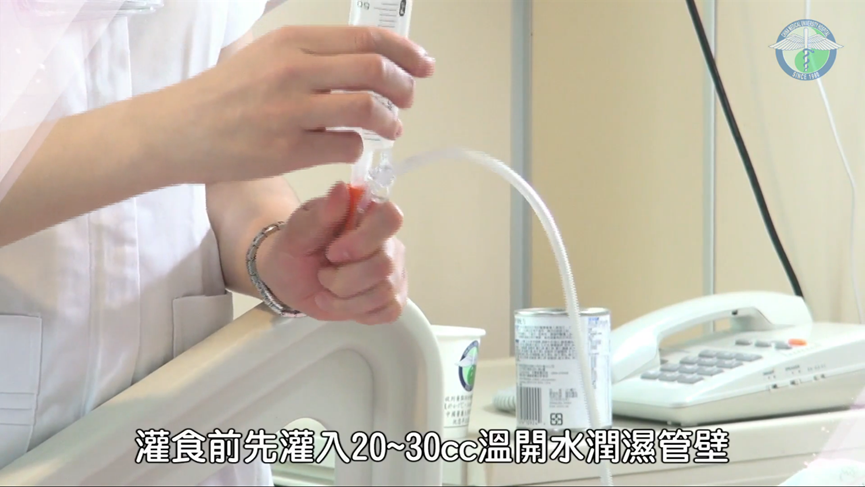
- Rinse the tube with 20-30ml warm water before proceeding to tube feeding.
- Hold the syringe tube up to 30-45cm from the patient’s nose. Allow food to slide into patients’ stomach slowly with gravity. The procedure should last at least 15 minutes.
- Avoid abdominal distension and there should be no air pumped into patients’ stomach.
- The feeding must be stopped when patients suffer from abdominal distension, pain, vomiting, coughing, or breathing difficulty. Comfort patients first and take them to the hospital immediately.
- In order to avoid the tube being clogged, 20-30ml warm water will be used to irrigate the tube after feeding.
- Bend the feeding tube and put it into the end of tube or close the opening after feeding. To avoid complications like vomiting, have patients sit up or take a semi-follow position at least 30 minutes.
- Do not come in contact with any irritating activities like suction, precaution, position change, passive exercises, and steam inhalation.
- Provid nasal and mouth care for patients and change the tape of the fixed tube everyday.