In Taiwan, liver cancer has been ranked first two places of top ten cancer mortality over more than 20 years, which affects the health of people substantially. According to statistics, there are new cases of 9,000 patients with liver cancer each year while there are approximately 8,000 patients who die of liver cancer each year.
Symptoms
There is no pain nerve inside the liver and hence there is usually no significant symptom at the early stage of liver cancer. Usually when patients perceive anomaly and then take examination at the hospital, it would be too late.
Some symptoms may gradually appear following the progress or cancer condition or size of tumor and occurrence location:
- Upper abdominal pain and bloating.
- Fatigue, poor appetite, and weight loss.
- Jaundice: The white of the eyes (sclera) and skin become yellow.
- Edema in lower limbs and ascites: Due to impairment of liver function, insufficient protein synthesized by liver. The fluid outflow in blood vessels accumulating massively into peritoneal cavity with symptoms of abdominal bloat, enlarged abdominal circumference, poor appetite, pitting edema in lower limbs, increased weight, decreased urine, nausea, vomiting, and general fatigue.
- Hematemesis: Esophageal or gastric variceal bleeding caused by liver cancer (portal hypertension), resulting in tarry or bloody stool, and in some severe cases with massive hematemesis.
- Acute abdominal pain: Liver tumor rupture and bleeding, resulting in the abrupt and intense pain in the abdomen, which could result in shock and fainting.
If liver cancer with metastasis to other areas of the body, it could cause other symptoms. For example, the bone pain caused by metastasis to the bone, and the cough and hemoptysis caused by metastasis to the lung.
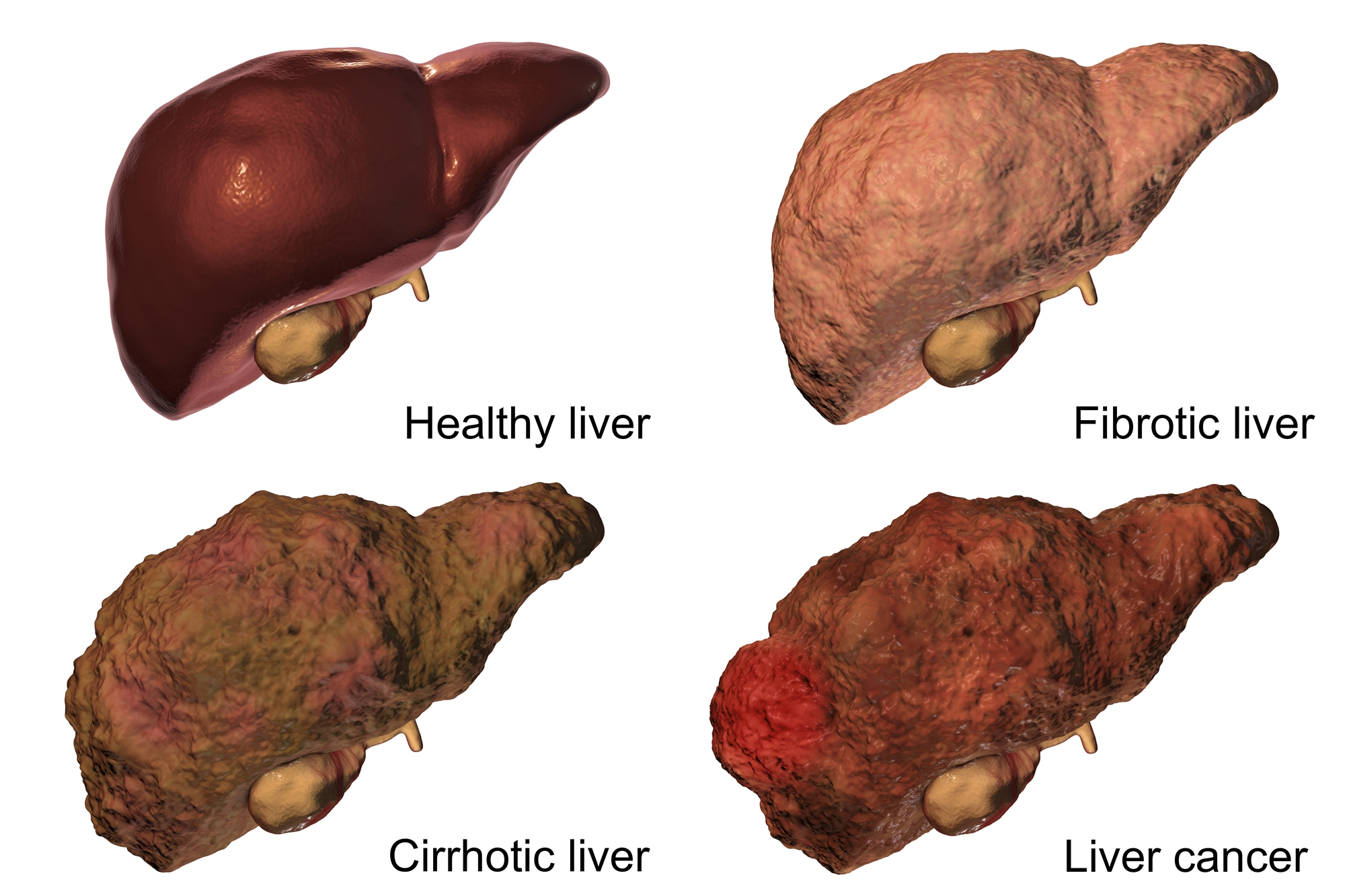
Cause of Liver Cancer
At least 90% of patients with liver cancer are related to liver cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis B or C, or excessive-drinking liver disease. In the so-called three-step procedure of “chronic hepatitis →liver cirrhosis→ liver cancer,” the probability of liver cancer generation caused by the DNA or RNA of virus or related protein directly is smaller, while majority is related to the repeated and chronic necrosis-based inflammation in liver. The out-of-control repair later leads to the generation of liver cancer and is related to the timeline and age when suffering the disease.
The high risk group susceptible to liver cancer is:
- Carrier of hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus.
- Patients with chronic hepatitis.
- Patients with cirrhosis.
- Family history (the first or second kinship) liver cancer.
How to prevent?
The most important key to prevent liver cancer is keep alcohol or virus away from the body. Second, patients already suffered from chronic hepatitis B or C should regularly follow up by blood drawing and abdominal ultrasound examination in order to detect earlier and engage in proactive treatment.
Considerate Reminders
If patients have hepatitis B or C or have family history of liver cancer and liver cirrhosis, such patients are suggested to take regular checkup for follow-up at the hospital in every half of a year, in particularly for the abdominal ultrasound examination.
Abdominal ultrasound examination could detect the liver cancer approximately 1cm in size and is the one indispensable tool for diagnosis.

