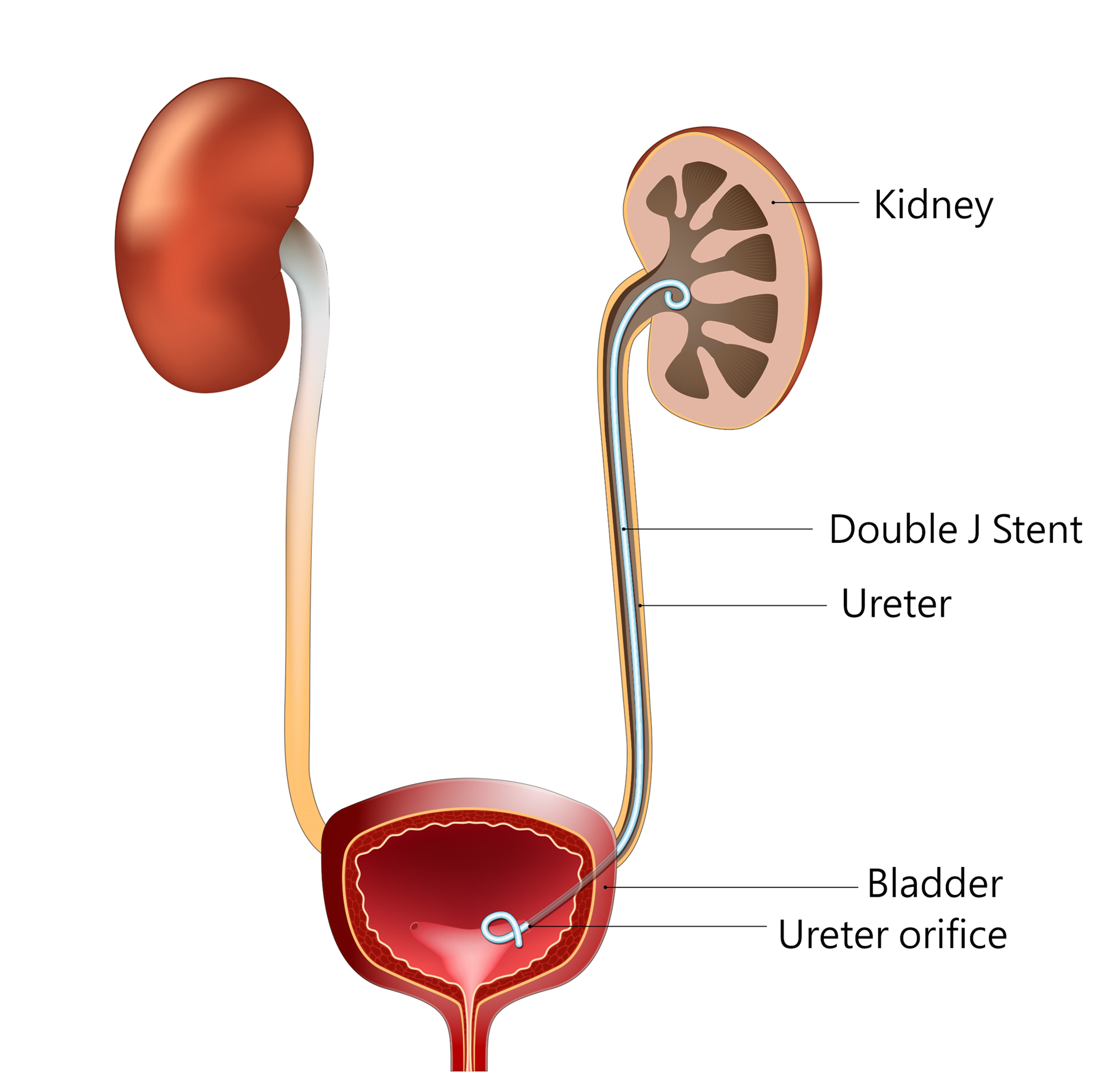
Indications for Double-J Stent Placement
- To allow urine to flow smoothly from the kidney to the bladder, keeping the ureter unobstructed and alleviating hydronephrosis.
- To prevent urine leakage from surgical wound sites and to promote ureteral healing.
Possible Side Effects
- Hematuria (blood in urine): The insertion procedure may cause minor bleeding, leading to blood in the urine.
- Urinary symptoms: Frequent urination, urgency, painful urination, or incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Pain: Discomfort or pain in the lower back or abdominal area.
- Infection: The procedure may cause bacterial infections or inflammation.
- Ureteral narrowing: Difficulty inserting the stent due to ureteral stricture.
- Stent displacement: The stent may shift or dislodge on its own.
Postoperative Care Instructions
- Drink 2,000–3,000 ml of fluids daily (including any beverages) to prevent hematuria and urinary tract infections. Patients with fluid restrictions should follow their doctor's advice.
- Do not hold in urine, as this may cause urine to flow back to the kidneys through the stent.
- Consume more vegetables and fruits to prevent constipation.
- Avoid prolonged standing, sitting, squatting, stretching, or any activities that increase abdominal pressure, such as sit-ups, straining during bowel movements or urination, and lifting heavy objects, to prevent hematuria or stent displacement.
- If you notice hematuria, reduce physical activity, rest, and drink more water. Monitor the color of your urine. If bright red blood persists in your urine, return to the clinic immediately.
- General stents: Double-J stents should not remain in the body for more than three months. If long-term use is required to manage hydronephrosis, stents are generally replaced every three months. Failure to replace stents regularly can lead to stone formation or complications during removal.
- Attend follow-up appointments as scheduled to allow your doctor to assess the condition of the stent and arrange for its removal or replacement as needed.

