Common causes of ascites
- Cirrhosis
- Congestive heart failure
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Malnutrition
- Infectious peritonitis
- Cancer with peritoneal invasion
Indications of paracentesis
- For differential diagnosis and decision making
- For decompressing the intra-abdominal pressure and relieving the discomfort
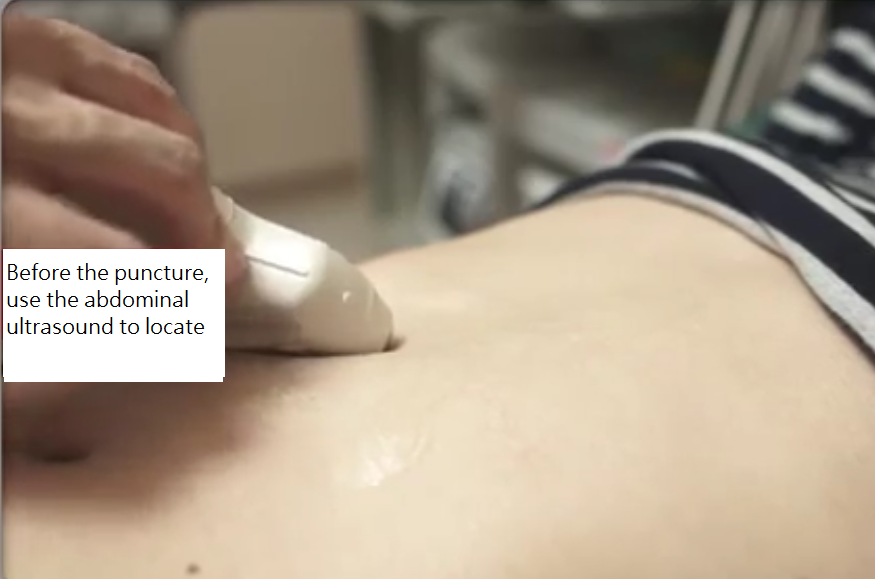
The procedure
- Please read the consent form and providing clear description of complications of Paracentesis for Ascites before the examination.
- The patients usually require neither sedation or Nothing by Mouth.
- During the procedure, the patients should to lie down and expose their abdomen.
- Ascites location by abdominal sonography before paracentesis.
- After cleaning the side of the abdomen with antiseptic solutions, physicians will insert a needle along with a plastic sheath to reach the ascitic fluid.
- The needle will be removed and, leave the plastic sheath behind to allow drainage of the fluid.
- The physicians should monitor the discomforts of patient and the color of ascites during paracentesis.
- After the procedure, the plastic sheath will be removed.
- The puncture site is covered with aseptic dressings and gauze.
Aftercare
- Monitor symptoms like dizziness and excessive pain, and patients’ vital sign.
- Change the dressings if there is any excessive oozing from the puncture site.
- Follow up on the abdominal circumference and body weight.

