Department Introduction
Department of Medical Imaging | Our Speciality
:::
Our Speciality
General X-ray imaging diagnosis is a routine examination or first-line screening. Currently common radiological examinations include CT, MRI, angiography, ultrasound, and interventional neuroradiological examinations.
With the advent of preventive medicine in the 21th century, the department teams up with the Physical Examination Center in developing an integrated medical imaging examination to provide more reliable and high quality inspection services required for the evaluation of common cardiovascular diseases and malignant tumor detection. We have designed and provided special imaging examinations for tumors, nerves, and hearts as cancer, cerebrovascular disease and heart disease are the first three causes of death in Taiwan. In addition, we have devised a local focal examination of the liver, lungs, or breasts for individual needs.
The division's outstanding special medical technologies are described as follows:
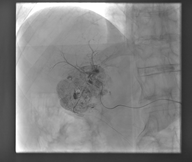
(1) Transhepatic arterial chemoembolization, TAE
TAE is a diagnosis and treatment method of blocking the blood vessels of the nutritional liver cancer and reducing the damage to the normal liver as far as possible. In principle, the treatment effect for patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma is better.

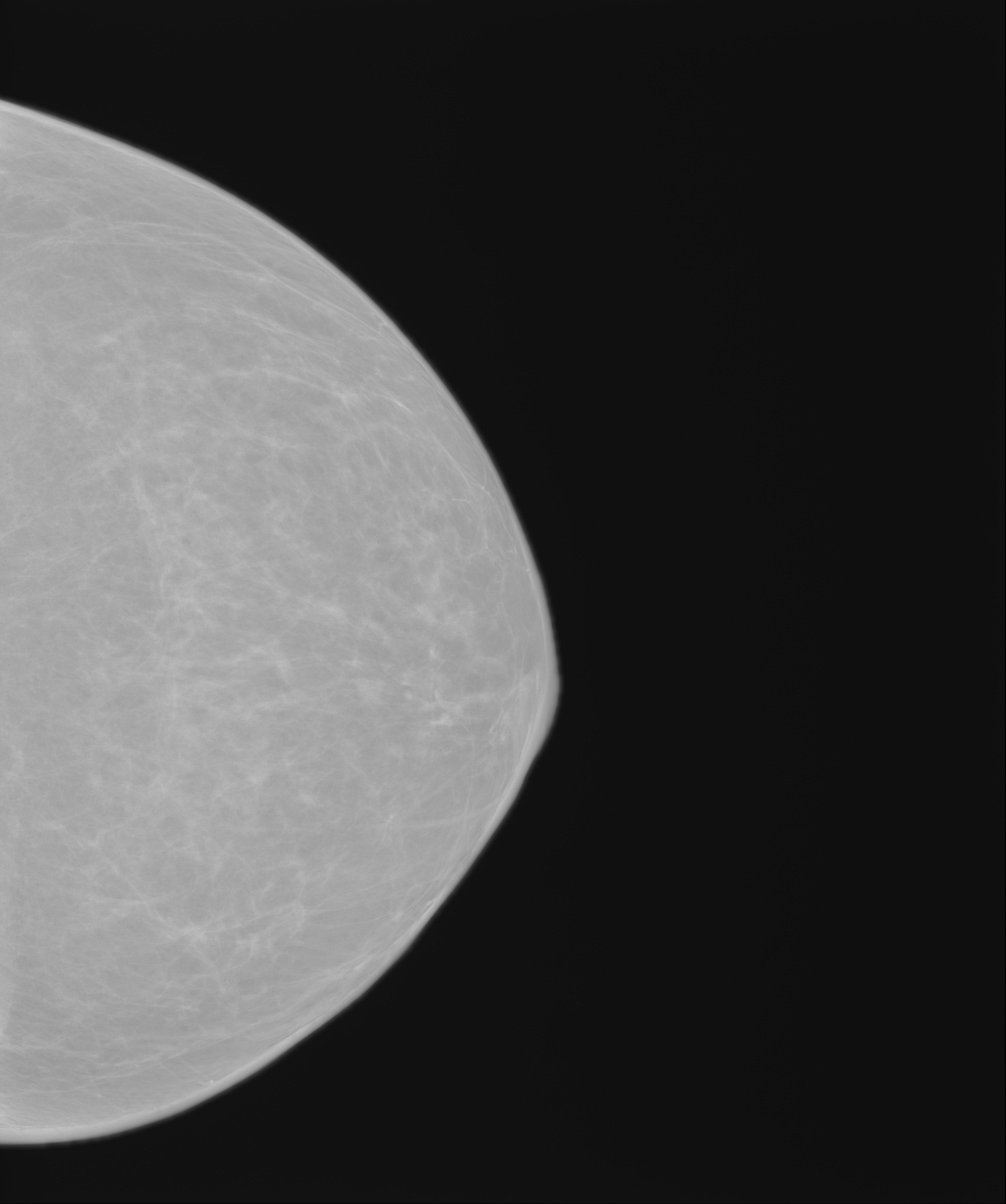
(2) Mammography
Mammography is a screening tool that has been confirmed to be able to effectively reduce the mortality of breast cancer. It can detect small calcification and then diagnose early-stage breast cancer. Mammography uses radiation to pass through the chest's fibrofatty tissues, lobular lactiferous ducts, blood vessels, and other related tissues and the soft tissues of the human body will show gray images while hard or dense tissues show a relatively white image. The image of a black and white plane is produced by the difference of the tissue, displaying a 2D image of a stereoscopic object.
The department has introduced digital mammography machines to transmit images immediately to the physician's room via the exclusive network. The high-quality X-ray photographs of the breasts are presented in front of doctors at fastest speed, providing them a basis for accurate diagnosis.

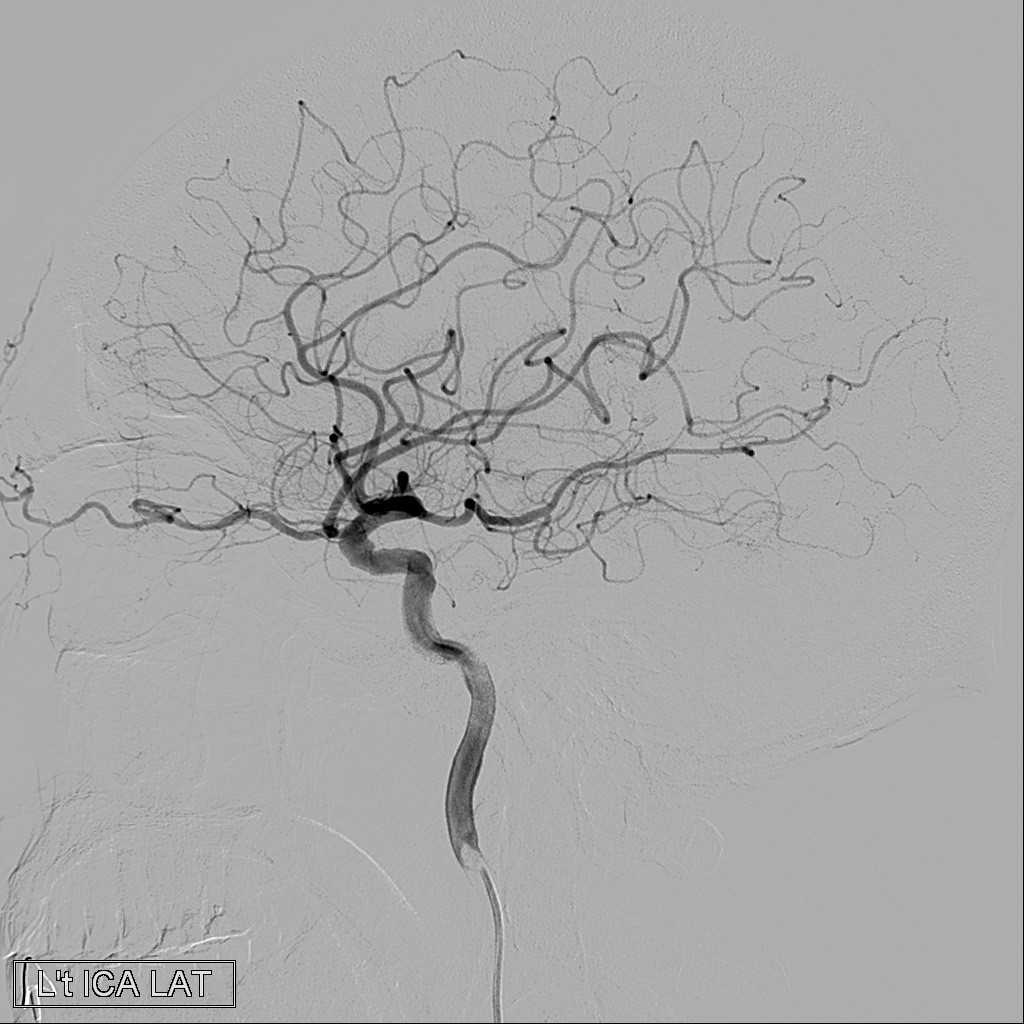
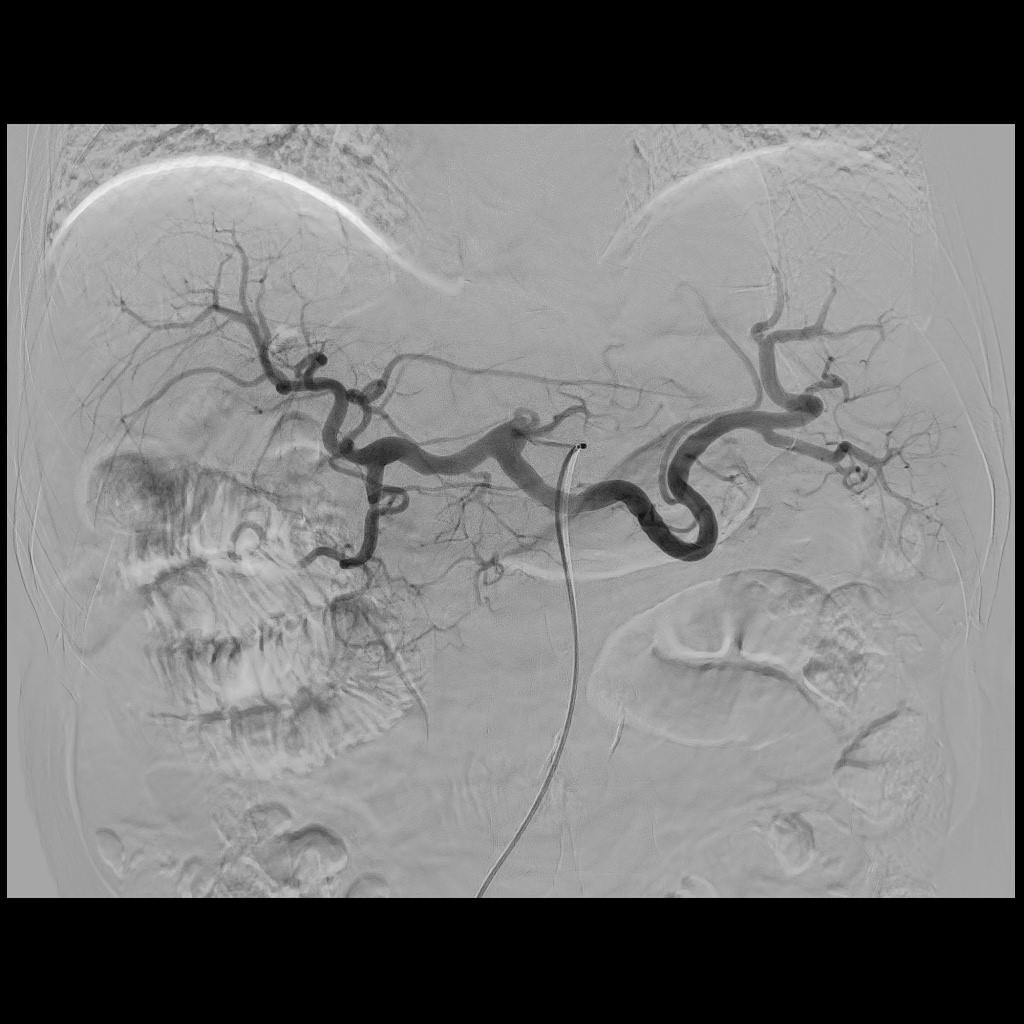
(3) Angiography
Angiography is the radiographic visualization of the blood vessels after injection of a radiopaque substance with an automatic syringe by sending some special catheters to the entrance of the blood vessel to be examined. Angiography is divided into "arteriography" and "venography" according to the characteristics of human blood vessels; for example, urological examinations via intravenous injection are for the examination of the kidneys, the urinary tract, the bladder, and other organs. The method of examination is to infuse the contrast agent into the body through the vein to get to the kidney via the blood circulation, which is then discharged from the kidney to the urine collection system. It can check the condition of the urinary system.


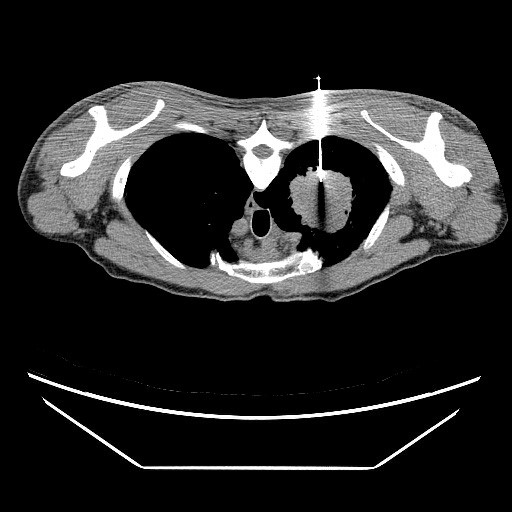
(4) CT-guided biopsy
CT-guided biopsy uses the CT instrument and radiography guidance and with the subcutaneous puncture introduces the lesion and extracts the biopsy sample for carrying out pathological examination. It can be applied to the lungs, liver, pancreas, lymph nodes, retroperitoneum, pelvic cavity, spine or other lesion locations. The advantage is that it can get enough tissue samples after highly accurate positioning and reduce postoperative complications, with a success rate of about 69% to 93%.

▲
