Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Center | Our Speciality
Our Speciality
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy was mostly applied to decompression sickness, known as divers' disease in the past. Over the last decade, it received more attention and promotion, with the scope of therapy expanded. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can provide unintended efficacy for refractory diseases.
The volume of air bubbles in the body is reduced by using the principle of pressure and gas volume size. Clinically, such a principle is mainly used to treat decompression sickness and arterial gas embolism.
High-concentration oxygenation in plasma causes vasoconstriction and is able to control the cavity pressure of the injured limb and the interstitial edema in the transplanted tissue. Clinically, such a principle can be used to treat compartment syndrome crush and contusion injury, acute burn, and cerebral edema.
By utilizing the principle of the action of peroxide, the efficacy of destruction and inhibition of the growth of bacteria is achieved, and the phagocytosis of white blood cells is increased. Clinically, this principle can be used to treat gas gangrene and wounds that are difficult to cure or heal, such as osteomyelitis and diabetic foot.
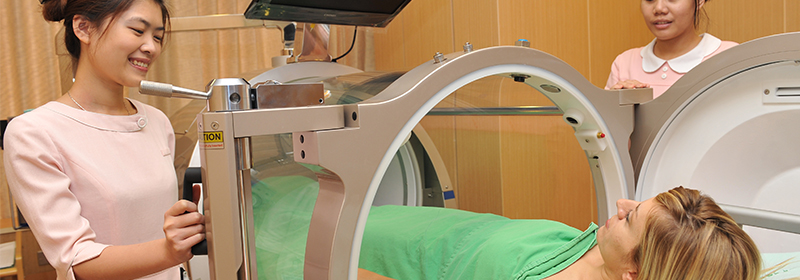
Carbon monoxide poisoning and decompression sickness noted above fall into the category of emergency medicine, while the rest are in interdisciplinary areas such as from surgery and orthopedics. The center founded in 2000 adopted a multiplace hyperbaric oxygen chamber, with a capacity of 12 persons. The center is composed of many undersea and hyperbaric medical specialists and professional nursing technicians in combination with divisions of vascular surgery, plastic surgery, general surgery, neurosurgery, orthopedics, dermatology, neurology, and oral surgery for jointly offering patients high-quality medical services.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is an excellent treatment under proper operation, but it can also cause injury if not used properly. While receiving hyperbaric oxygen therapy, it is necessary, depending on the circumstances, to cooperate with internal medicine therapy or surgical debridement to get a good therapeutic effect. Therefore, the integrated team of hyperbaric oxygen therapy needs considerable training and professional cognition.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is subject to the evaluation and confirmation by a hyperbaric oxygen specialist before the therapy session can be arranged. The therapy is medical treatment in which the patient is placed in the hyperbaric chamber which is then pressurized to a certain atmospheric pressure. The patient inhales 100% of pure oxygen through a mask to boost the oxygen concentration in the blood and improve histanoxia, as well as kill anaerobic bacteria and promote wound healing for the purpose of treatment. In principle, the disease should be treated once a day, with about 80 to 120 minutes each time. The number of treatment sessions to be received needs to be evaluated and confirmed by the attending physician.
( Refer to the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society)
- Gas embolism
- Carbon monoxide poisoning and acute smoke inhalation injury
- Gas poisoning (carbon monoxide, gas poisoning, hydrogen sulfide, cyanide, benzene poisoning, etc.)
- Anaerobic bacterial infection (e.g. gas gangrene)
- Acute trauma (acute run-over injury, acute trauma, surgical wound healing)
- Decompression sickness
- Chronic wounds (diabetic foot ulcers, bedsore, vascular lesions, etc.)
- Specific anemia
- Brain abscess
- Sudden deafness
- Chronic osteomyelitis, osteonecrosis, poor bone healing, etc.
- Radionecrosis (including soft tissue, bones, and internal organs)
- Critical skin or flap tissue transplantation, etc.
- Burns
- Other hypoxic diseases
- Diver's disease (decompression sickness) or acute gas embolism
- Carbon monoxide poisoning (cyanide and gas poisoning)
- Gas gangrene
Necrosis of gas gangrene and anaerobic bacterial infection
Soft tissue infection and mixed bacterial infection - Chronic recurrent osteomyelitis
- Limb crush injury accompanied by traumatic hemorrhage
- Acute burn injury accounts for over 15 percent of the body surface area
- Radionecrosis
Osteoradionecrosis
Radiation enteritis
Radiocystitis


