Leptospirosis, an infection caused by Leptospira, is a common zoonotic disease in tropical and subtropical regions.
Mode of Transmission
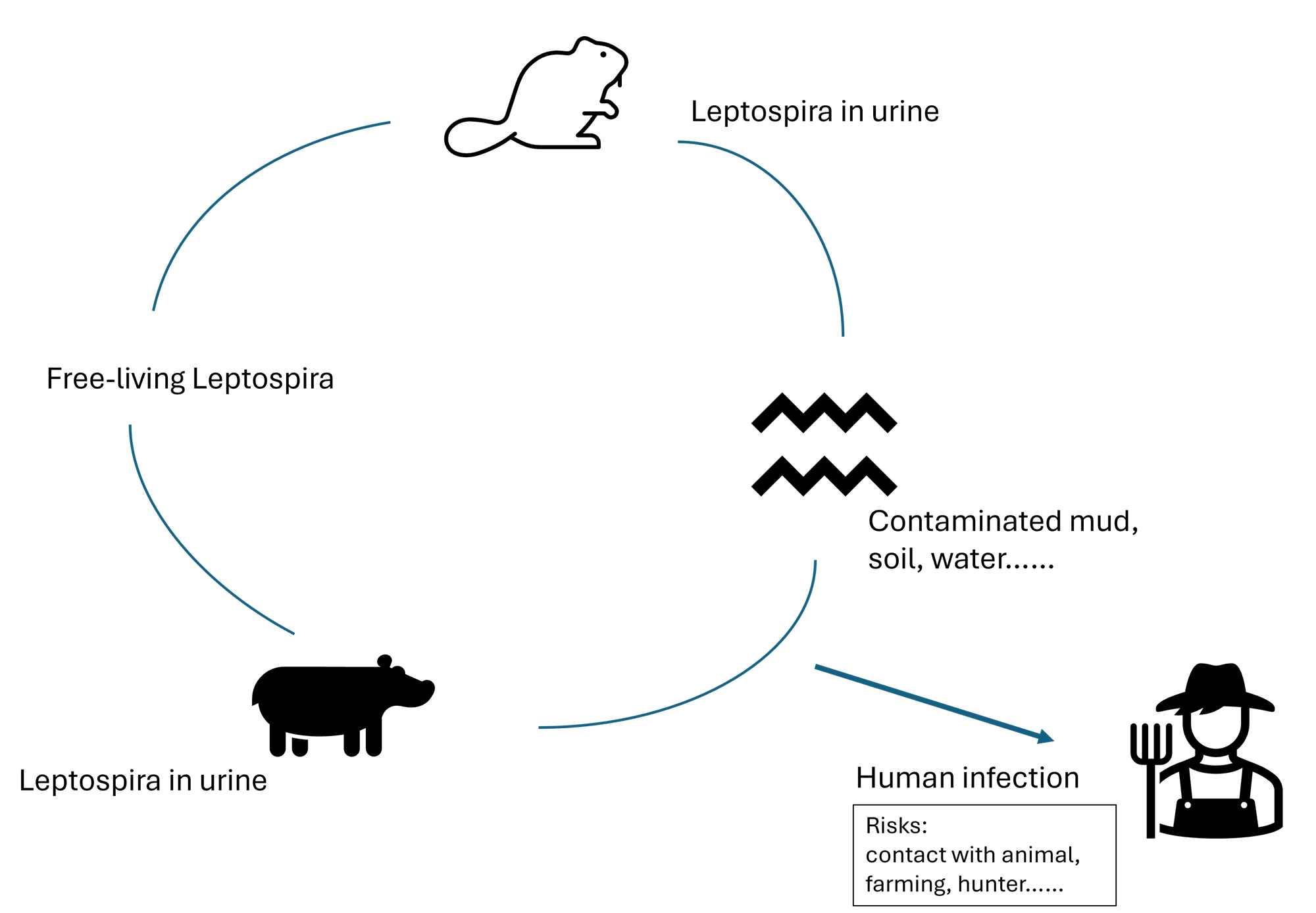
Infection by ingesting or coming into contact with water, soil or food contaminated with the urine or tissues of infected animals. Infection of wounds through skin wounds, oropharyngeal mucosa, eye conjunctiva, nasal cavity or genital tract when people are working (e.g. farmers, sanitary sewer workers or maintenance workers, miners), swimming, paddling in the water or camping.
Clinical Symptoms
The clinical symptoms of an infected person can vary from asymptomatic to mild to severe. In mild cases, symptoms are similar to those of a cold, including fever, headache, gastrointestinal discomfort, chills, red eyes, muscle aches and pains, and meningitis in some cases, while in severe cases, kidney failure, jaundice, myocarditis or bleeding, or even death.
Therapy
Antibiotics and active supportive treatment, including respiratory therapy, fluid control and electrolyte balance, as well as bleeding management, and dialysis if renal failure occurs.
Precautions
- Avoid contact with water or soil that may be contaminated.
- Take appropriate protective measures, such as wearing boots, gloves and aprons, when work must be exposed to the source of the disease.
- Keep the home environment clean, isolate infected animals and avoid urine contamination.

