Tracheotomy is used to treat obstruction of the upper respiratory tract, so that the respiratory tract temporarily communicates with the outside via the trachea directly, without passing through the nose, throat, laryngopharynx and other parts.
A person who suffers from hypoxia and asphyxia for more than three minutes may cause degeneration or necrosis of brain cells. Although tracheotomy is a seemingly simple operation, it also has some high risks.
Indications
- Those who need long-term tracheal intubation.
- Those with poor cardiopulmonary function who often need sputum suction or oxygen delivery.
- Those with upper respiratory tract obstruction who are unable or difficult to receive tracheal intubation.
- Preoperative establishment of the respiratory tract in patients with head and neck tumors.
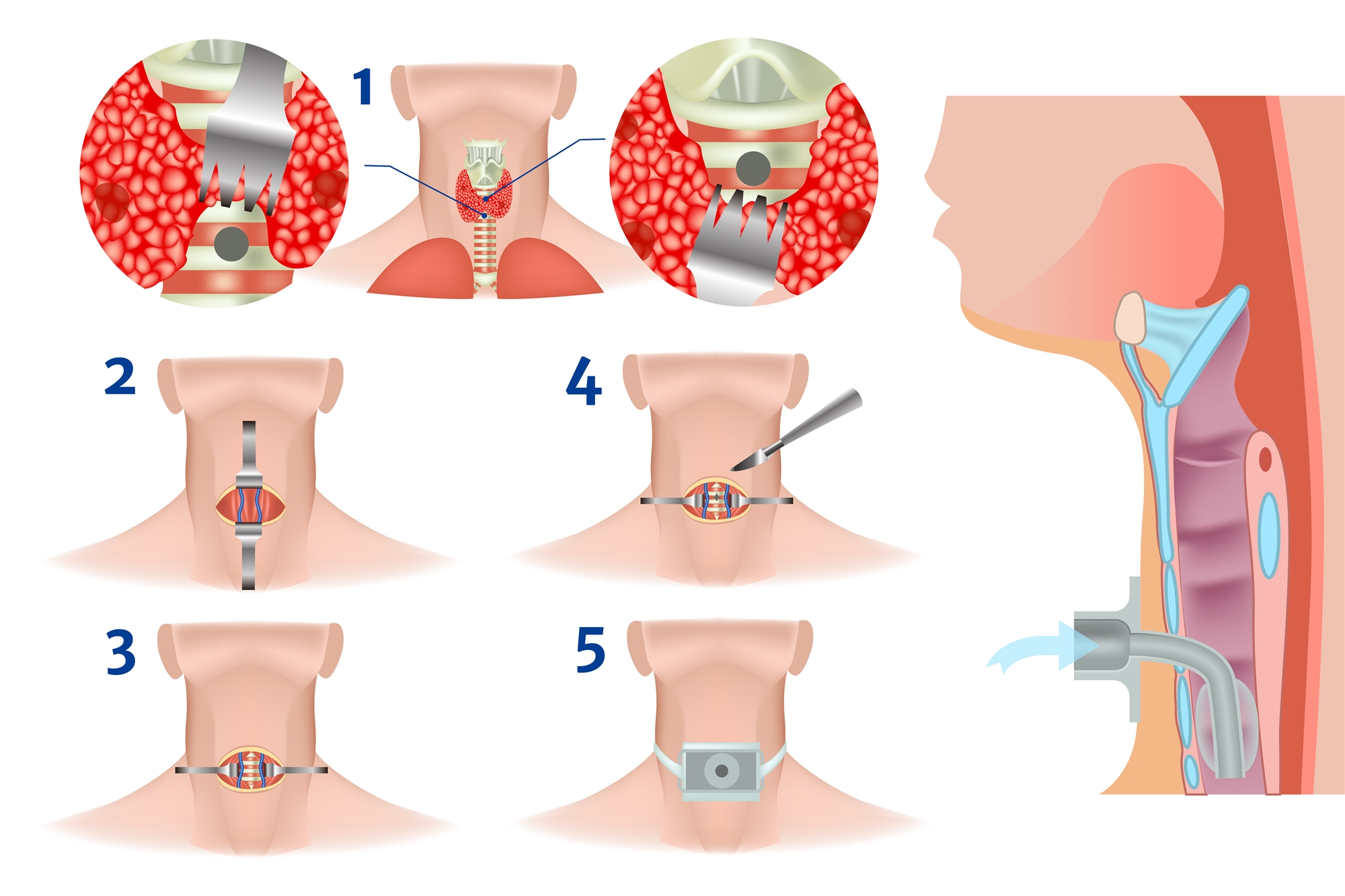
Operative Procedures
- Incise the skin in the middle of the neck.
- Peel off the tissue layer by layer and separate the subcutaneous layer, pretracheal muscle and thyroid gland to expose trachea.
- Cut open the anterior tracheal muscular membrane to expose the second and third, tracheal rings.
- Insert a breathing cannula after the trachea is incised in an appropriate position, and then fix the cannula to the neck.
Possible Comorbidities
- Immediate complications: hemorrhage, pneumothorax, misplaced tracheal cannula, and Injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerves.
- Medium-term complications: tracheitis and tracheal bronchitis, tracheal erosion and bleeding, hypercapnia, atelectasis, tracheostomy tube displacement, tracheostomy tube obstruction, subcutaneous emphysema, wound cellulitis.
- Delayed complications: tracheal stenosis, tracheoesophageal fistula, tracheomalacia, tracheal granulation tissue, dysphagia, tracheal skin fistula, etc.
Postoperative Observation and Care
- If there is massive bleeding, breathing with phlegm sound, voice in mouth, tube slipping, neck swelling, abnormal agitation of the patient and other phenomena occur, the medical staff should be informed immediately.
- Within a few days after surgery, tracheal secretions increase, and more sputum should be sucked. If there is thick sputum obstruction, it will cause breathing difficulties. At this point, the cannula should be replaced.
- Once the cannula is removed, granulation tissue will form in the wound within 48 hours, so if the cannula slips, it should be replaced as soon as possible.
- When a metal tube is put in place, the inner one should be cleaned regularly every day, while the outer one should be replaced by boiling and disinfection at least once a week.
- Once out of the respirator, the patient should practice to cough up the sputum or suck out the sputum through a tracheotomy to reduce the chance of respiratory obstruction, asphyxia and pneumonia.
- The balloon inflation of the tracheal cannula need not be too tight, because long-term inflation will give lasting pressure to the tracheal mucosa, resulting in mucosal ischemia and erosion. In the absence of wound bleeding or other inhalation, the balloon should maintain appropriate pressure.

