Ultraviolet (UV) radiation treatment (phototherapy) uses special wavelength UV light to irradiate the skin and regulate the immune response to produce therapeutic effect on your disease.
Which Patients Need UV Phototherapy?
Patients with psoriasis, leukoplakia, atopic dermatitis, skin lymphoma, pruritus caused by hemodialysis and other indications can be treated with phototherapy. But phototherapy does not cure these diseases, it can only alleviate them.
UV Phototherapy Process
Generally, there will be so-called initial doses of radiation, which will be adjusted according to individual needs. When irradiation is initiated, the dosage increases gradually until the skin becomes slightly red and hot.
UV radiation treatment requires patient cooperation, and regular and quantitative treatment will have the best effect. Two to three treatments per week should be given, with each at least 24 hours apart.
UV Phototherapy Side Effects
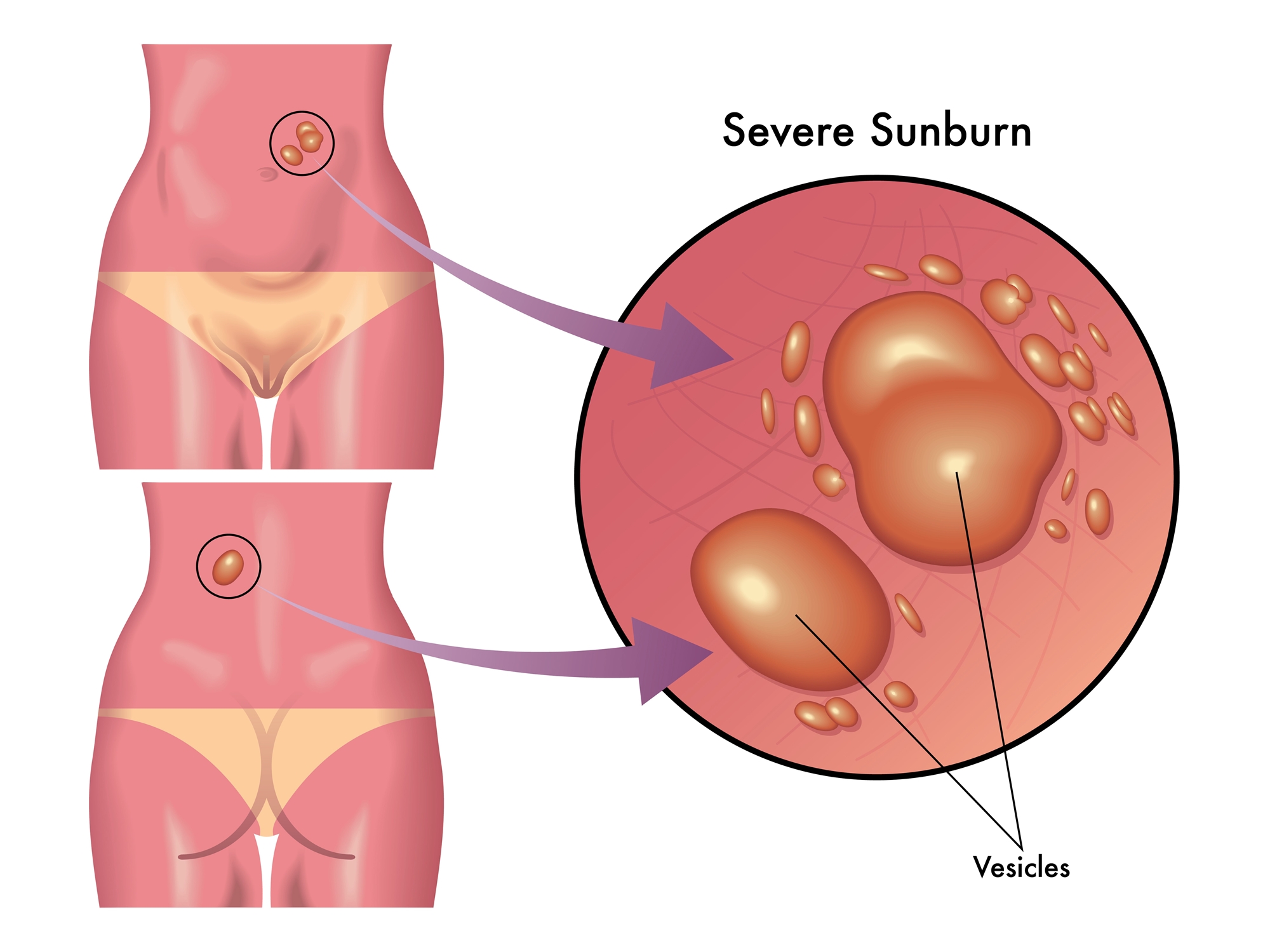
The most common side effects of UV phototherapy are sunburn, temporary dryness of the skin or itching. Be sure to tell your doctor when you develop erythema or sunburn during treatment. The doctor will adjust or postpone the treatment plan for you depending on the severity of the injury. Some patients with light sensitivity may develop a sudden fever and headache, while a few (e.g. with lupus erythematosus) may be aggravated by the therapy. Be sure to inform your physician if you have similar illnesses.