Scrotal edema refers to hydrocele testis that expands the tunica vaginalis and causes scrotum to enlarge. Scrotal edema is a common urinary disease in newborns with 6% of incidence rate. The testicle is surrounded by a water bag like sac in the scrotum. The size of edema depends on the amount of liquid, ranging from the size of scrotum to as big as a baseball.
Causes
There are congenital scrotal edema and acquired scrotal edema. The causes are as follow:
- Congenital Scrotal Edema: Occurs in newborns. When testicles drop to scrotum from abdomen, it brings down the peritoneum along and form vaginal process. Normally the vaginal process closes up automatically. If the vaginal process stays open, the contents of abdomen will enter the vaginal process and lead to enlarged scrotum. When the opening of vaginal process is small and only allows liquid to flow through, it causes scrotal edema. If the opening is big enough for the intestine to enter, hernia may occurs.
- Acquired Scrotal Edema: Often occurs in adults. The causes for acquired scrotal edema include trauma, impact on scrotum, radiation therapy, acute and chronic epididymitis, tuberculosis invades the testicles, or epididymis. Besides, males under the age of 40 year-old should watch out for testicle tumors when scrotal edema occurs because tumors stimulate and causes scrotal edema. 10% of testicle tumor cases have symptoms of scrotal edema.
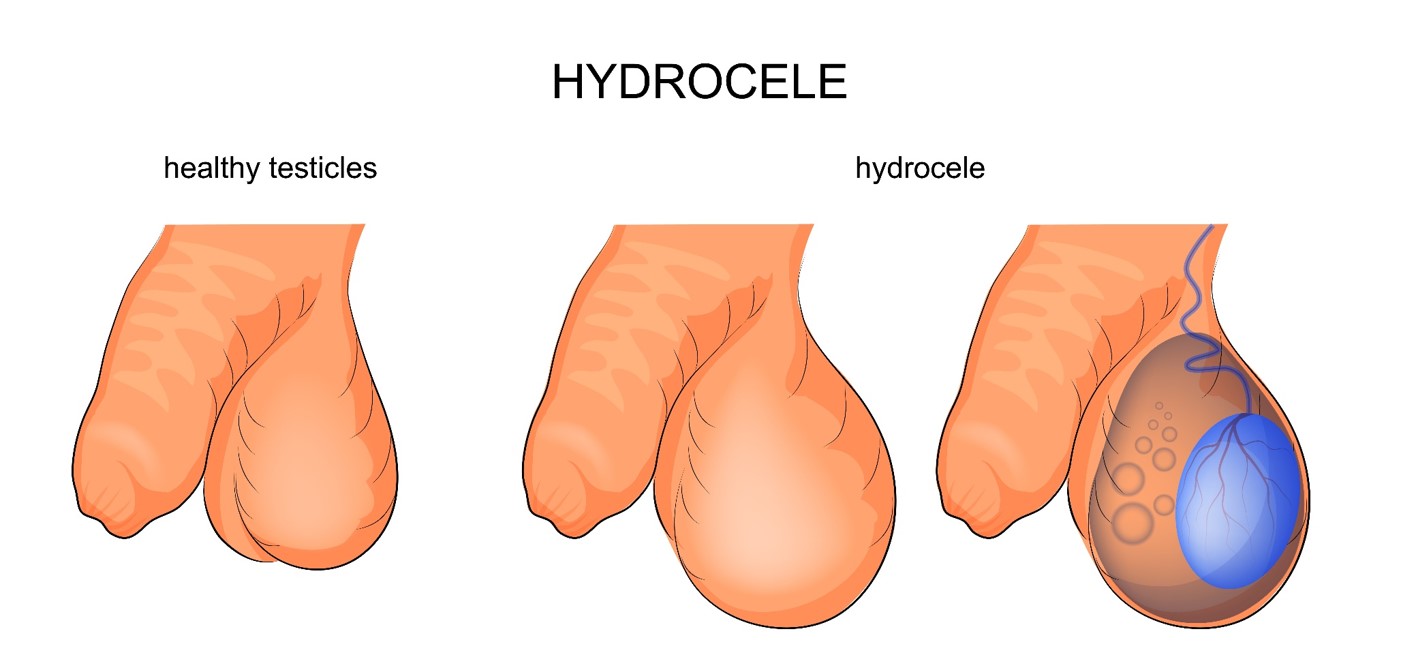
Symptoms
The scrotum appears to be swelling or one side is larger than the other. The size of scrotum changes for congenital scrotal edema. It is smaller and softer in the morning and becomes larger and tighter in the evening. Scrotal edema sometimes comes with swelling pain.
Diagnosis
- Physical Checkup
Feel the liquid inside tunica vaginalis when touching testicles. Scrotum becomes transparent under the light when scrotal edema occurs. If not transparent, it could be hernia or testicle tumor. Further diagnosis is required.
- Ultrasound
Ultrasound is the best for diagnosis to identify tumor or edema.
Treatment Timing
Vaginal process usually closes up before age of one. Thus, keep close observation and let it run its course. If it does not close up after age of one, then treatment is needed. When adults have scrotal edema, immediate treatment is required.
Treatments
- Operation as scrotal approach
- For congenital scrotal edema in children, surgery on groin is performed to find the vaginal process and perform ligation. The vaginal process is removed after pumping out all the liquid. For adults, surgery is performed on the scrotum for hydrocelectomy.
Conclusion
Children with scrotal edema often have low self-esteem. Parents should make close observation when giving them a bath. Seek for help from urological physicians when issues are observed.
For adults with scrotal edema, patients should look out for tumor and seek for proper treatments.

