Overview
Tonsillitis is an infection or inflammation of the tonsils. The palatine tonsils are structures of lymphatic tissue on both sides of the throat, above and behind the tongue. They are part of the immune system, which helps the body fight infection. Tonsillitis often goes away on its own after 4 to 10 days.
Causes
Most often, acute tonsillitis is caused by a virus. Less often, it is caused by bacteria that cause strep throat. In rare cases, a fungus or a parasite can cause it. In chronic tonsillitis ( intermittent symptoms that persist over time ), there is a long-standing infection that is usually bacterial.
Symptoms
- Symptoms of acute tonsillitis include:
- the rapid onset of severe sore throat that worsens over time
- moderate to high fever
- difficulty in swallowing
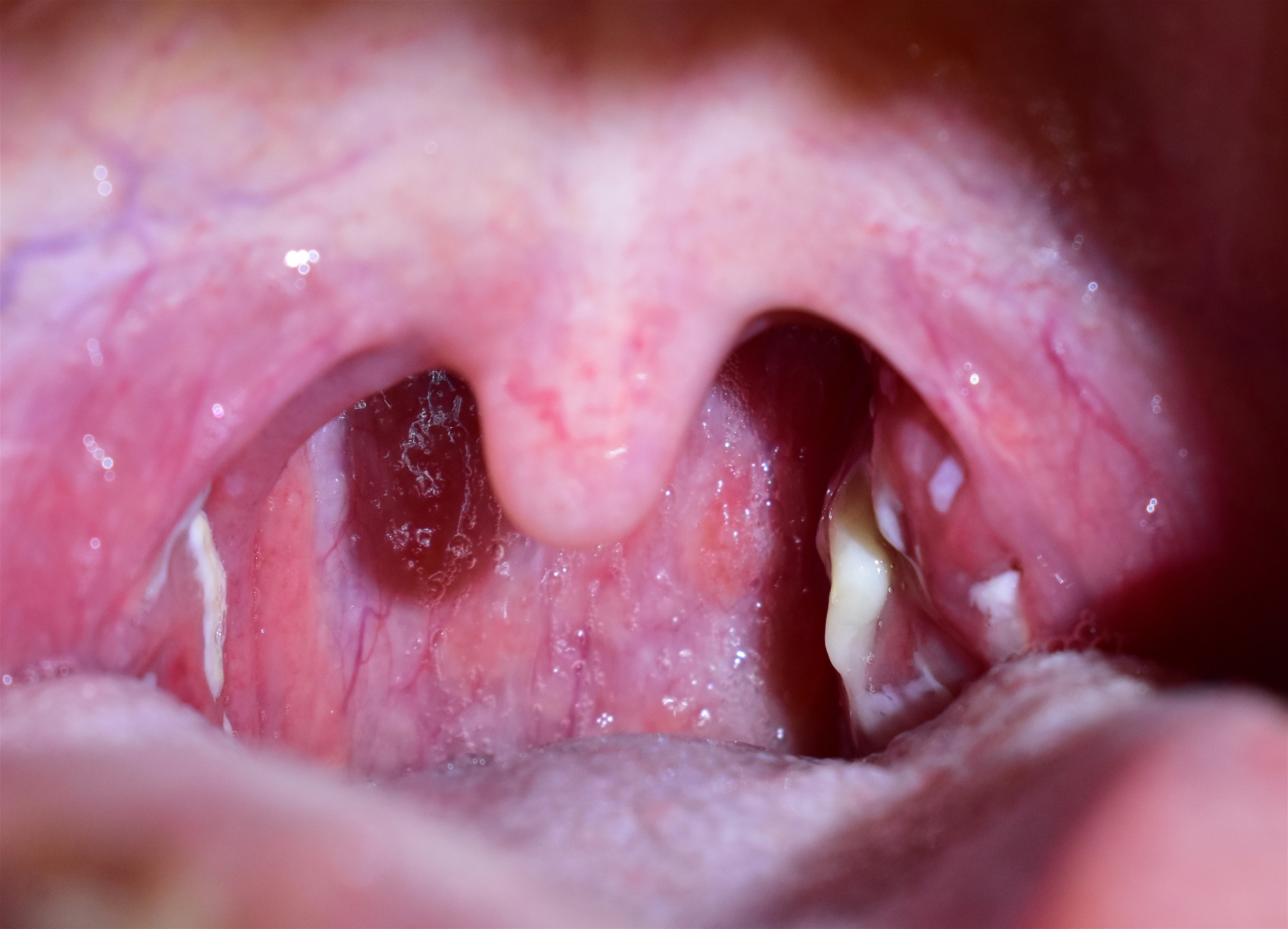
- red, enlarged tonsils that may or may not have pus on the surface or in the pits
- swollen or tender lymph nodes below the jaw
- Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis include :
- enlarged, mildly red tonsils that are scarred with large pits
- slightly enlarged lymph nodes that are not usually tender
- sore throat that comes and goes
Diagnosis
Your doctor will look at your throat to see if you have red and swollen tonsils with spots or sores. These signs mean that you have tonsillitis.
Treatment
Tonsillitis caused by a virus will usually go away on its own. Treatment focuses on helping you feel better. You may be able to ease throat pain by gargling salt water, drinking warm tea, and using other home treatments. Over-the-counter pain medicines, such as acetaminophen may also be used. If your tonsillitis is caused by bacteria ( such as streptococcus ), you need treatment with antibiotics. Antibiotics can help prevent rare but serious problems caused by streptococcus and can control the spread of infection.
As a rule, doctors only advise surgery to remove tonsils (tonsillectomy) when there are serious problems with the tonsils.
These include:
- Recurrent infection ( > 3 times per year for 3 years; > 5 times per year for 2 years; > 7 times per year for one year)
- Peritonsillar abscess or deep neck infection
- Unilateral tonsilar hypertrophy or suspect of tumor
- Hypertrophy of tonsils that causes the problem during daytime activities such as swallowing problem or sleep disorders.
- Tonsillitis could cause severe complications such as rheumatid fever and nephritis
Prevention
- You may be able to ease throat pain by gargling with salt water, drinking warm tea, and avoid smoke and wine intake. Drink plenty to avoid dehydration.
- Post-tonsillectomy recovery can take from 10 days up to a month, during which narcotic analgesics are typically prescribed. You may usually be advised not to eat "crunchy" or "rough" food (toast, biscuits, cookies, and crackers) as they may scrape the back of the throat, and increasing the risk of bleeding or infection after the operation. Spicy and acidic foods are irritating and should be avoided. Proper hydration is very important during this time, since dehydration can increase throat pain, leading to a vicious cycle of poor fluid intake.

