What is larynx
Larynx is an organ with a function phonation composed of bone, cartilage, and soft tissue. It locates just above the tracheal. The main functions of larynx are breathing, swallowing and phonation.
Risk factors
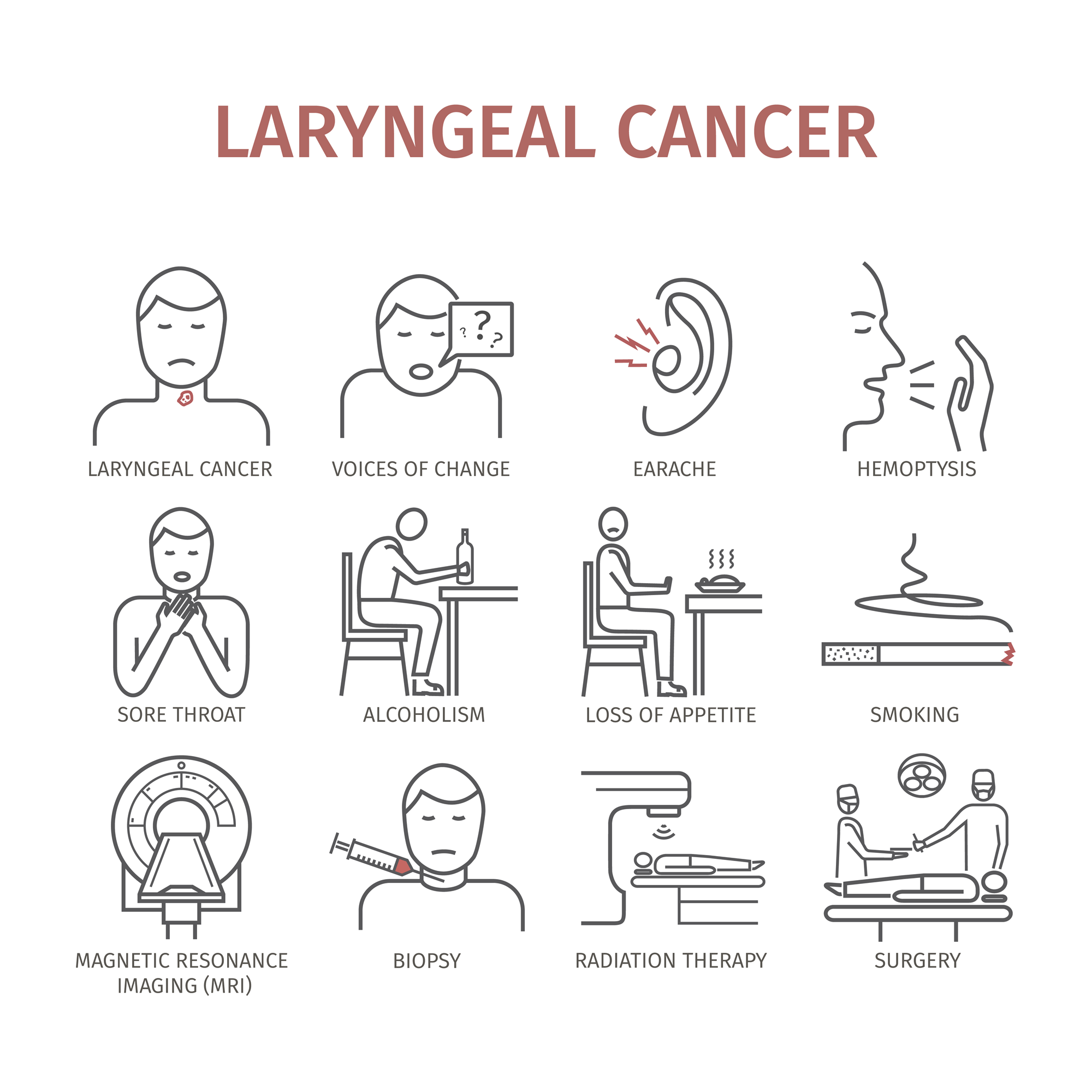
The incidence of laryngeal cancer is higher in male than female. It usually occurs between ages of 40 to 70 years. It is related to heavy smoking and alcohol intake. Most of the laryngeal cancer is squamous cell carcinoma in pathology (95%).
Symptoms and signs
Laryngeal cancer can be detected early. If you note that your hoarseness persisted for more than 2 weeks, you should meet your ENT doctor for further evaluation. Advanced stage laryngeal cancer may present with dyspnea and dysphagia because the tumor invaded the esophagus, tongue base or other laryngeal tissues. You may also find neck lymphnode enlargement that is possibly caused by metastasis of cancer cells. Furthermore, cough or bloody tinged sputum is also present due to tumor necrosis.
Diagnosis
If a patient has symptoms suspect of laryngeal cancer, the doctor will put a tube with a special light on the end of it down to the patient’s throat to look at the larynx. This procedure is called laryngoscopy. If there were abnormal tissues in larynx, the doctor will take a small piece of the tissue and look at it under the microscope to see if it contains any cancer cells. This procedure is called a biopsy, and it is the only way to confirm a cancer diagnosis. If a patient has cancer of the larynx, the doctor will do more tests (such as Chest X-ray, head and neck CT scan, bone scan, and abdominal echo) to find out if cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body. This process is called staging, and it helps the doctor to plan the treatment strategy for each patient.
Treatment
Early stage laryngeal cancer could be treated by partial laryngectomy or radiation therapy alone for preserving laryngeal function. But patients with an advanced stage laryngeal cancer should better receive total laryngectomy combined with radiation therapy and chemotherapy. And if there is neck lymphnode metastasis, further neck dissection is also necessary.
Rehabilitation
Voice restoration after Laryngectomy can reduce the inconvenience of communication. The most common tool is pneumatic speech aid, and there are still electronic speech aid and the artificial valve; and a small number of people can even use the esophageal voice without any aids. All of the above can significantly reduce language dysfunction after total laryngectomy.

