Causes of cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of dermis and subcutaneous tissues, layers of the skin, caused by Streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, which enter through cuts on the lower limbs and open injuries like surgical wounds, ulcers, or scrapes; sometimes it causes systemic infection if bacteria circulate via blood and lymph system.
Clinical symptoms
Cellulitis symptoms include redness, heat, and swelling pain; without timely treatment, the infected area might have necrosis and suppuration which may trigger fever and white blood cell numbers increase; with severe patients, it may lead to gangrene, necrotizing fasciitis, and sepsis of the affected limb.
Cellulitis treatment
To contain infection, doctors often prescribe antibiotic; before the treatment, it is recommended to undergo blood cultures or local secretion cultures. If the cultures yield positive result, doctors may readjust antibiotics for more precise treatment. After 1-3 days proper antibiotic treatment, symptoms often subside and most patients can be cured 7-14 days later.
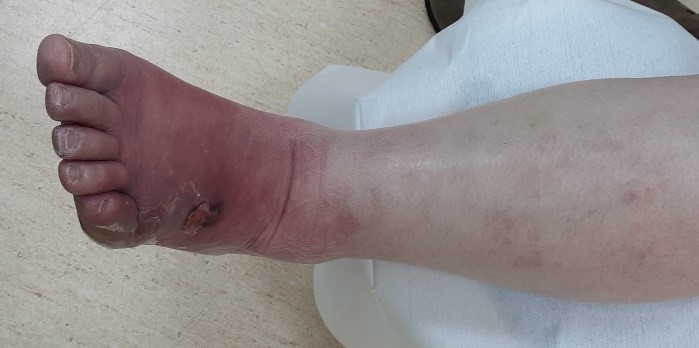
Tending methods
- Patients should be well rested and raise the infected area to promote venous blood return and to reduce edema.
- Closely observe the redness, temperature, and pain condition of the infected area.
- For open injuries, surgical aseptic technique is adopted to tend the infected area; for the changed dressing, it should be packed inside bags with contagious sign for later incineration.
- To relieve the ache of the infected area, follow doctors’ advice in taking analgesic.
- Get more bed rest, and avoid standing for an extended periods.

