What is hepatitis B?
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, with accompanying liver cell damage or cell death; it is caused most frequently by viral infection, certain drugs, chemicals, or poisons. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver.
Why is hepatitis B a terrible disease?
In Taiwan nearly half of the adults have been infected by HBV, and about 15~20% of them are chronic HBV carriers. Approximately 20~30% of these chronic carriers may progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer. Therefore, HBV carriers are 100 times more likely to develop liver cancer than non-HBV carriers.
Transmission routes of HBV
- Vertical transmission—HBV is transmitted vertically from HBV carrier mothers to infants during the perinatal period.
- Horizontal transmission—HBV is transmitted through blood transfusion, intravenous drug use, ear-piercing, tattooing, and body piercing. It is also transmittable through sharing instruments such as toothbrushes, razors, and nail scissors.
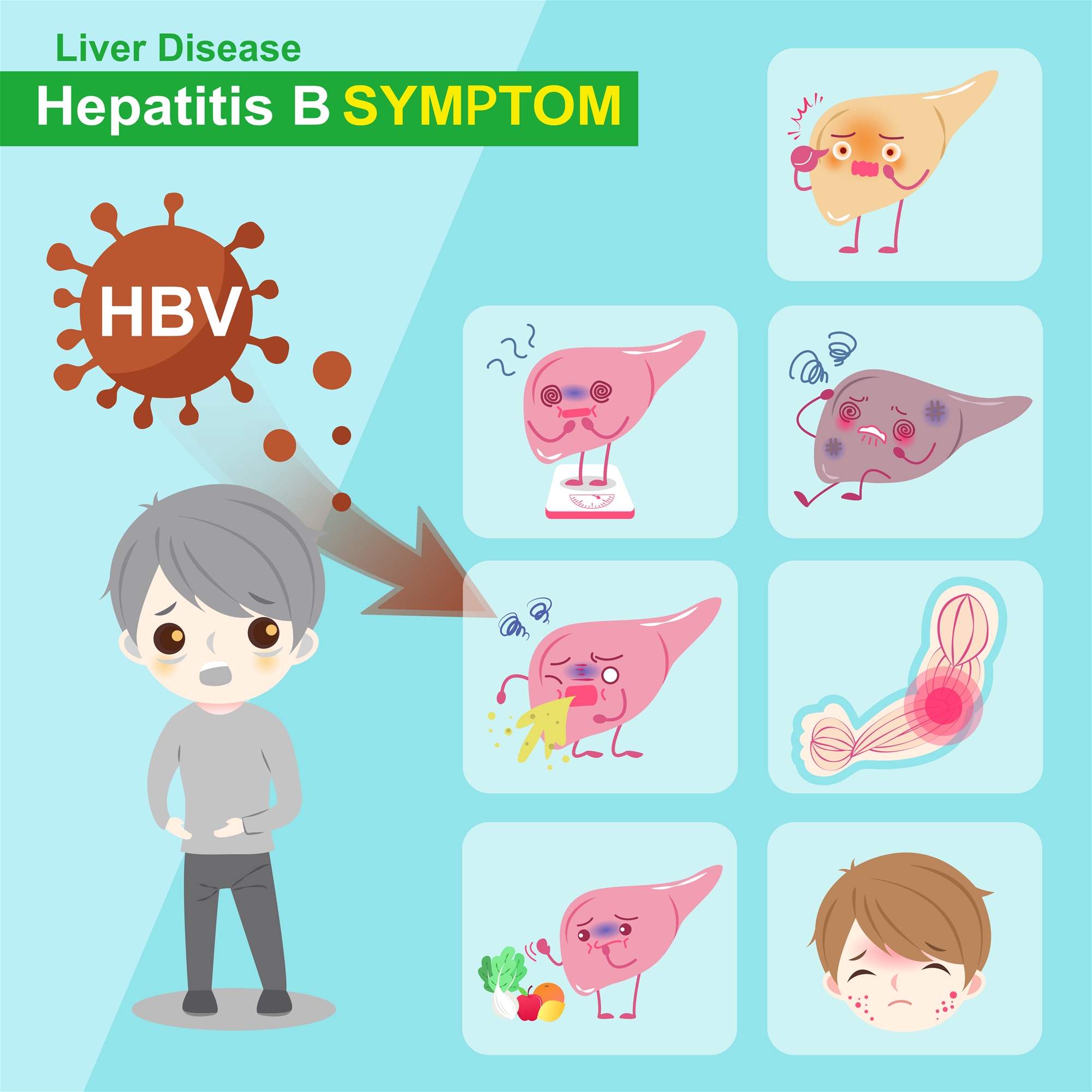
What are the symptoms of hepatitis B?
Many people infected with viral hepatitis have no symptoms. About one-third of people infected with HBV have a completely "silent" disease.
- Incubation period of the HBV is about three months.
- The most common prodromal symptoms are flu-like, fever, headache, myalgia, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal fullness.
- Late symptoms may include tea-colored urine, clay-colored stools, and yellowing of the skin (jaundice), and sclera of the eyes.
Dietary guideline for hepatitis B
Intake or supply food is suggested as follows:
- Garlic, legumes, onions, eggs, and other foods with high sulfur content.
- Water-soluble fibers such as pears, oat bran, apples, and legumes.
- Cabbage-family vegetables, especially broccoli, brussels sprouts, and cabbage.
- Artichokes, beets, carrots, dandelion greens, and many herbs and spices such as turmeric, cinnamon, and licorice.
- Green foods like wheat grass juice, dehydrated barley grass juice, chlorella, and spirulina.
- Balanced diet with healthy protein and healthy fat. Decrease alcohol intake.
- Discuss with physician or nutritionist about diet plan to prevent metabolic syndrome, fatty liver, and malnutrition.
Treatment and prevention for hepatitis B
- For patients with chronic hepatitis B, there are six frequently used medications including: pegylated interferon alfa-2a, adefovir dipivoxil (ADV), lamivudine (LAM), entecavir (ETV), tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF). Before starting such a treatment, consult with your physicians and have them evaluate your condition thoroughly.
- Intake plenty of fluid and nutritional supplement.
- Proceed to severe alcoholic restriction, hypnotics, sedatives, and herbs intake; better yet, avoid them completely.
- Avoid unnecessary blood transfusion and intravenous drug injection.
- Blood test for HBV carriage during pregnancy and children born to HBeAg-positive mothers must receive HBIG and its first hepatitis vaccine within 24 hours of birth.
- Live a relaxed life style and attain to exercise with a regular pace.

